Providing knowledge of the satellite-killer electrons in near-Earth space using a near real-time data driven space weather model based on ULF-wave radial diffusion.
Universe Today
-
NASA Commanded Psyche To Turn Around And Capture Images Of Earth And The Moon

New images from NASA's Psyche spacecraft show that its cameras are working just fine. By pointing them at Earth and the Moon, NASA was able to test the spacecraft's cameras and science instruments. Since both bodies reflect light like Psyche, and since their spectra are familiar, it's a valuable opportunity to test and calibrate the instruments.
-
Uranus' 29th Moon Can't Hide From The JWST

The JWST has found another moon orbiting Uranus. It's the planet's 29th known moon, and it bears the uninspiring, temporary name S/2025 U1. It's too small and faint to be detected by the Hubble, or by Voyager 2, the only spacecraft to visit the ice giant.
-
How the Apollo Missions Unlocked the Origins of the Moon
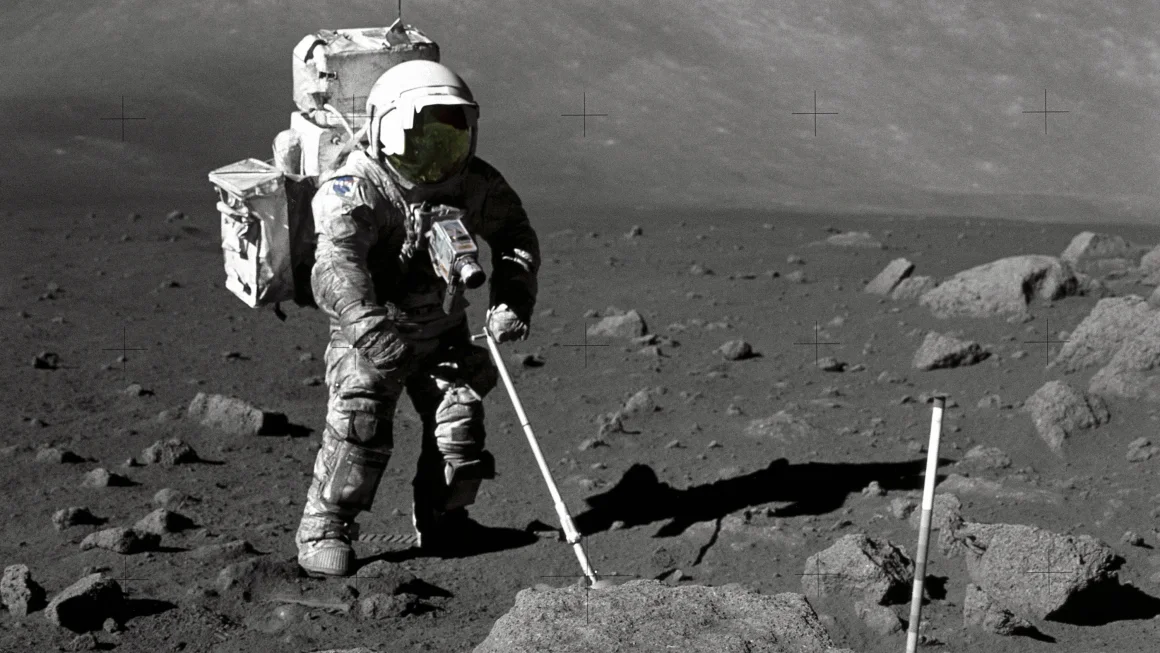

You know, if you think about it, and trust me we’re about to, the Moon is kind of weird.
-
Using Video Game Techniques To Optimize Solar Sails

Sometimes inspiration can strike from the most unexpected places. It can result in a cross-pollination between ideas commonly used in one field but applied to a completely different one. That might have been the case with a recent paper on lightsail design from researchers at the University of Nottingham that used techniques typically used in video games to develop a new and improved structure of a lightsail.
-
Advancing Lunar Habitats with Thermoelectric Power Generation
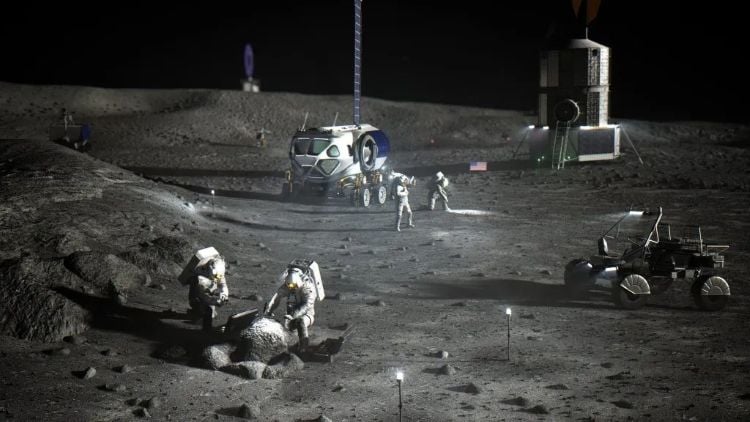

How can thermoelectric generators (TEGs) help advance future lunar surface habitats? This is what a recent study published in Acta Astronautica hopes to address as a team of researchers from the Republic of Korea investigated a novel technique for improving power efficiency and reliability under the Moon’s harsh conditions. This study has the potential to help mission planners, engineers, and future astronauts develop technologies necessary for deep space human exploration to the Moon and beyond.
-
Sensors Could Permanently Fly In The "Ignorosphere" Using Novel Propulsion Technique
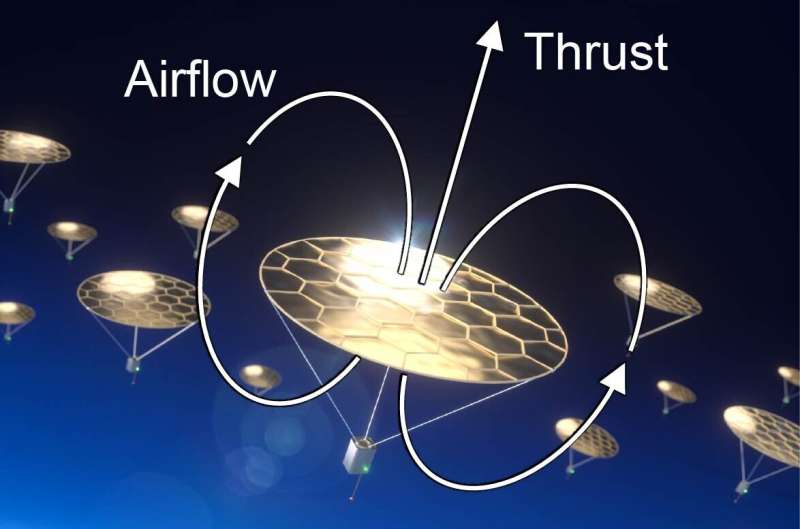
Earth’s atmosphere is large, extending out to around 10,000 km from the surface of the planet. It’s so large, in fact, that scientists break it into five separate sections, and there’s one particular section that hasn’t got a whole lot of attention due to the difficulty in keeping any craft afloat there. Planes and balloons can visit the troposphere and stratosphere, the two sections closest to the ground, while satellites can sit in orbit in the thermosphere and exosphere, allowing for a platform for consistent observations. But the mesosphere, the section in the middle, is too close to have a stable orbit, but too sparse in air for traditional airplanes or balloons to work. As a result, we don’t have a lot of data on it, but it impacts climate and weather forecasting, so scientists have simply had to make a lot of assumptions about what it's like up there. But a new study from researchers at Harvard and the University of Chicago might have found a way to put stable sensing platforms into the mesosphere, using a novel flight mechanism known as photophoresis.
-
New Study Suggests We Should Search for "Spillover" from Extraterrestrial Radio Communications
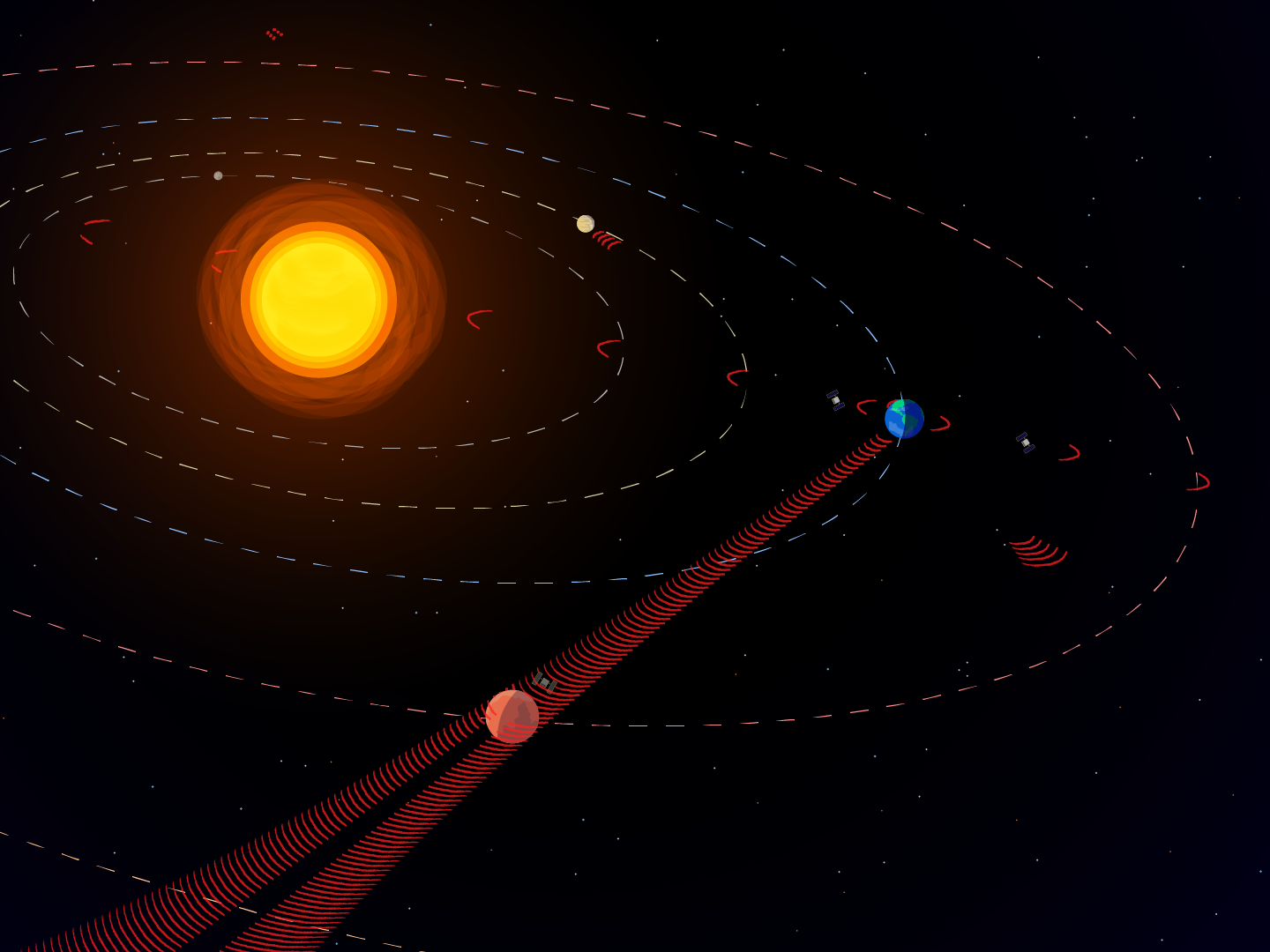
New analysis of human deep space communications suggests the most likely places to detect signals from an extraterrestrial intelligence.
-
These Rare Star Systems Are A New Tool To Understand Brown Dwarfs
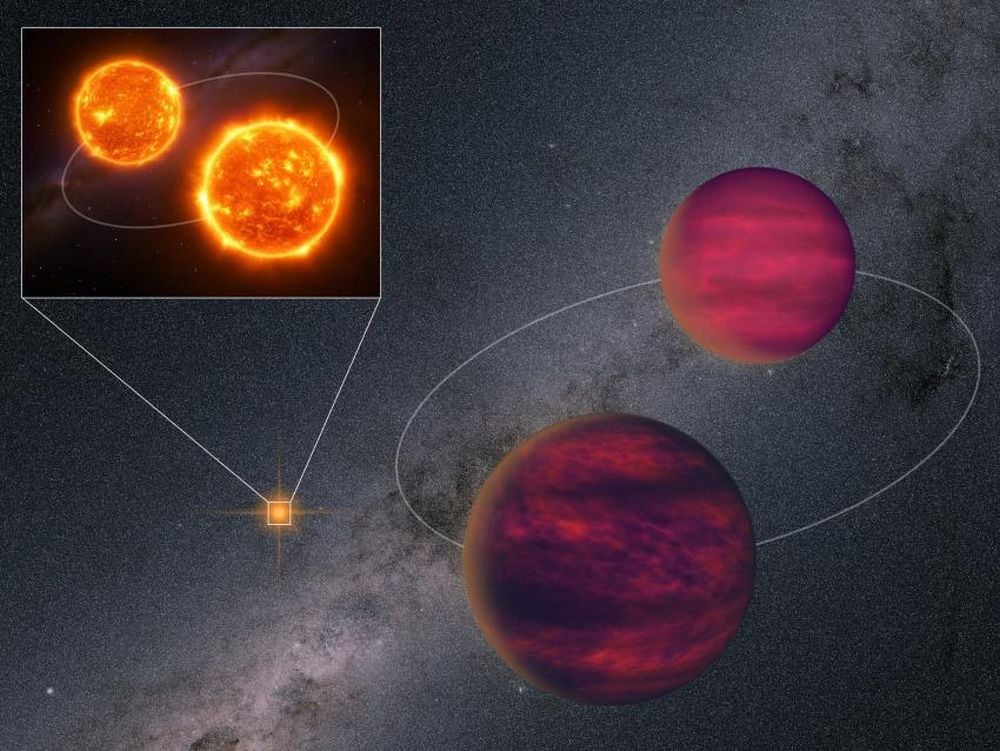
The discovery of an extremely rare quadruple star system could significantly advance our understanding of brown dwarfs, astronomers say. Brown dwarfs in wide binary orbits offer a chance to determine their properties more clearly.
-
The Moon’s Dirty Past
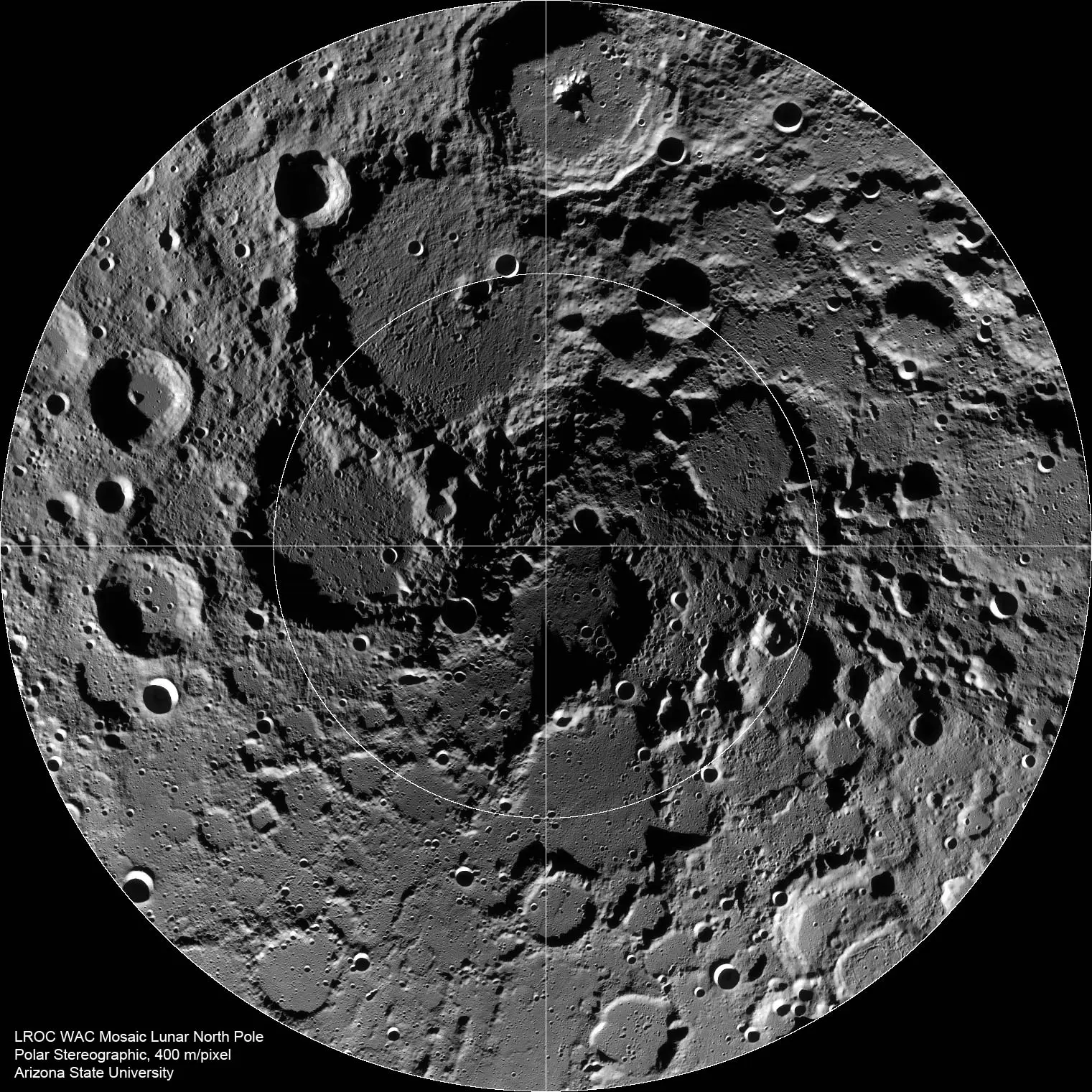

How do you tell how old an astronomical object is? I mean, the next time the Moon is in the sky, take a look at it. How would you even begin to answer that question?
-
NASA Researchers Show How Ceres Could Have Once Been Habitable
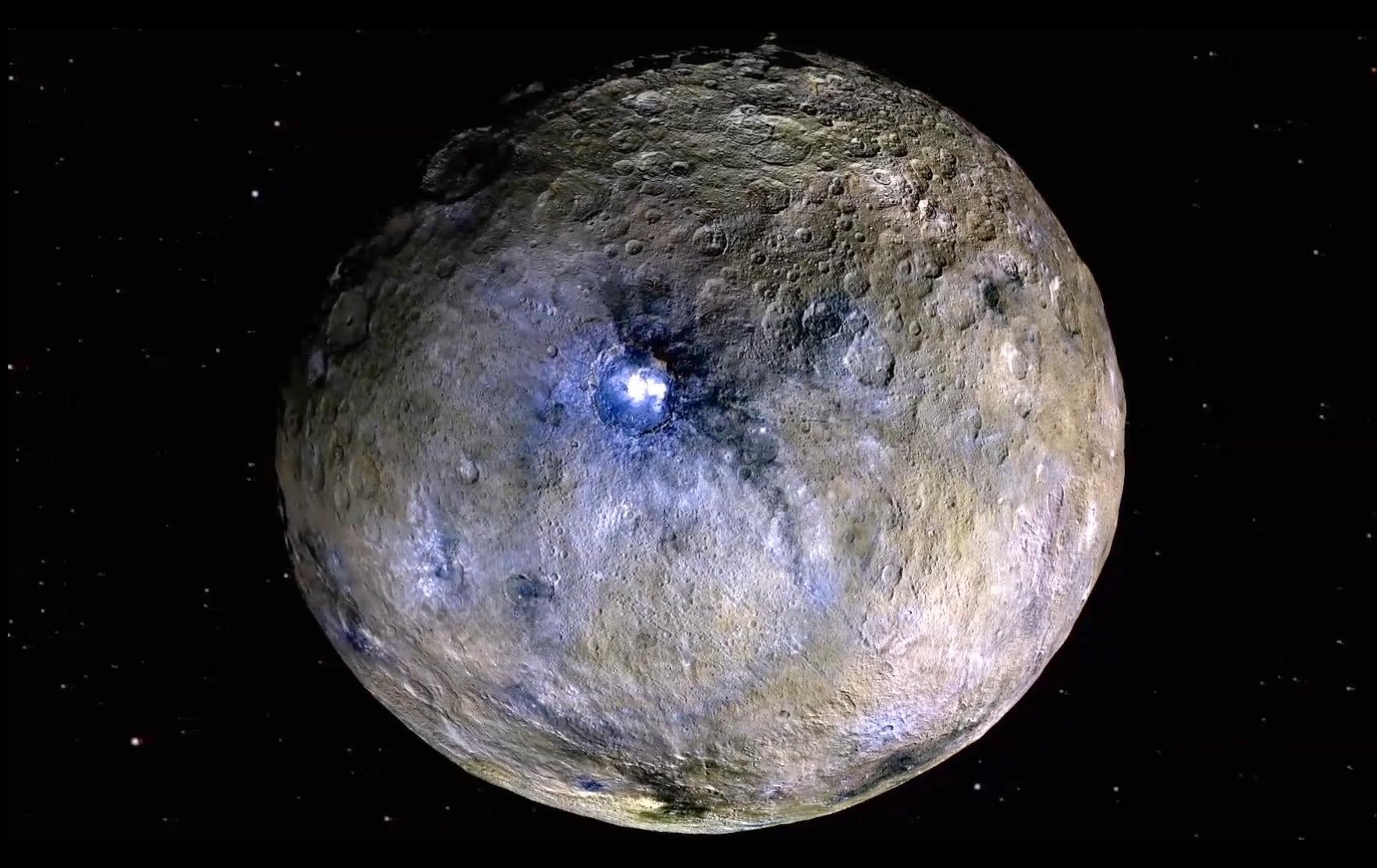

The dwarf planet is cold now, but new research paints a picture of Ceres hosting a deep, long-lived energy source that may have maintained habitable conditions in the past.